The classification of TiO2 three main types for plastics
Titanium dioxide is the mainstay white pigment for the global plastics industry. Mark Holmes speaks to three leading international consultants (Eric Bender from TZMI, Andriy Gonchar from RD Titan Group Innovative TiO2 and independent consultant Peter Waugh) to find their views on the current market for this vital product and the key trends influencing developments in the Compounding World 2016.
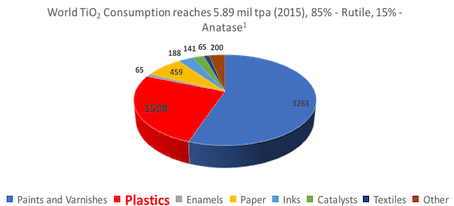
"The TiO2 demand in the plastics industry is around 1.5m tonnes per year, around 25% of global consumption. However, in the aim to understand the overall market for plastics and the companies that supply them, it is very important to understand characterization of different types of TiO2," says Andriy Gonchar, head at RD Titan Group.
World Titanium Dioxide Consumption by Industry
The RD Titan Group has created its own classification and has distinguished three main types[1] of titanium dioxide for use in the manufacture of plastics. This classification was formed over the past 20 years, influenced by the world's major producers of TiO2: Chemours, Huntsman, Cristal, Kronos, and Tronox. In fact, this is the answer of the top 5 global companies to the requests of their customers. Other TiO2 manufacturers toe the line of top 5 companies. A detailed classification of all grades of TiO2 is given in Comprehensive Dossier of the World's Titanium Dioxide Grades and TiO2 Manufacturers.
Plastic Type 1. This type of grade is characterized by special surface treatment using small amounts of aluminum compounds (or without any inorganic surface treatment) and special organic additives, which impart typically hydrophobic properties to the surface of pigment particles. This type of grades has been designed for maximum processability of pigments in plastics, and especially for the production of high temperature cast films, in which the use of other titanium dioxide grades is limited due to lacing. Durability of these grades can be estimated as low-medium.
Plastic Type 2. This type of grade is characterized by special surface treatment using aluminum compoundsand special organic additives, which impart typically hydrophobic properties to the surface of pigment particles. This type of grades has been designed for maximum pigment processability in the production of various kinds of plastics, especially for those applications wherein the dispersibility of pigment is a critical parameter. The durability of these grades can be estimated as medium.
Plastic Type 3. This type of grade is characterized by special surface treatment with aluminum and silicon (or sometimes zirconium instead of silicon or in combination with it) compounds and special organic additives usually imparting hydrophobicity to the surface of pigment particles. This type of grades has been designed for maximum pigment processability in the production of various types of plastics, for which durability is a critical parameter (for example, for the production of PVC window profiles). The durability of these grades can be estimated as superior.
Some manufacturers also use technologies of rutile crystal lattice doping to reduce its photochemical activity and improve durability.
Typical characteristics of TiO2 grades for plastics
| Plastics Type 1 | Plastics Type 2 | Plastics Type 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 content | 97-98% | 95-96% | 91-93% |
| Lattice | >97% of rutile | >97% of rutile | >97% of rutile |
| Surface coating | Alumina or not | Alumina | Alumina, silica (some companies use zirconia) |
| Organic treatment | Yes (Hydrophobic surface properties) | Yes (Hydrophobic surface properties) | Yes (Hydrophobic surface properties) |
| Applications | Polyolefin masterbatch; flexible PVC (interior), high temperature cast films, thin films; PVC plastisols | Polyolefin masterbatch; polyethylene; polypropylene; PVC (interior) | PVC and polyolefins (exterior, non-chalking); agricultural films; outdoor furniture; PVC window profiles |
| Relative scattering power | High | Superior | Medium high |
| Filter Pressure Value Test (EN 13900-5) | Low-medium (Lower value are better for use in masterbatches) | Low (Lower value are better for use in masterbatches) | Medium (Lower value are better for use in masterbatches) |
| Carbon black undertone | Blue-very blue | Very blue | Neutral |
| L*(CIELAB) in pressed powder | >96.5 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) | >97 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) | >97 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) |
| b*(CIELAB) in pressed powder | <2 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) | <2 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) | <2 (D65, spectrophotometer normalized be Net Profiles 3 tool) |
| Dispersibility in thermoplastics | High | Superior | High |
| Durability (weatherability) | Low-medium (Anatase grades have a low level of durability) | Medium (Anatase grades have a low level of durability) | Superior (Anatase grades have a low level of durability) |
| Lacing resistance | Superior | Medium | Low |
| ISD 591-1:2000 type | R1 | R2 | R2 |
| ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types | II | II | II, IV |
[1] A detailed classification of all grades of titanium dioxide is given in Comprehensive Dossier of the World's Titanium Dioxide Grades and TiO2 Manufacturers. http://innovativetio2.com/dossier/ Year 2016, -