China titanium dioxide industry: current status and following steps.
The current state of TiO2 products in China. Comparison with the Top-5 products of western producers of TiO2.
The technical side of the coin.
Part-1
1. China TiO2 Industry: a giant leap for the last two decades
China titanium dioxide industry for two decades has made an amazing leap. In 1995 all the production capacity of TiO2 in China has been distributed among several small factories which has produced mainly anatase grades of titanium dioxide and totaled about 130,000 MT per annum. And by the end of 2014 in China, we have 46 companies which own 56 plants for the production of TiO2 with Effective Capacity 2,750,000 MT per annum and the actual release of more than 2,300,000 MT per annum. The growth of power in 20 years amounted 2015%, and growth of the actual release amounted 1770 %. At the same time the consumption of titanium dioxide in the world increased by 67% from 3.4 million tons in 1995 to 5.7 million tons in 2014. Today China is the largest titanium dioxide producer in the world. In 2003 Effective Capacity of China plants of TiO2 reached 500,000 MT per annum and in four years in 2007 doubled in relation to 2003, reaching 1,000,000 MT tons per annum; in 2011it again doubled in relation to 2007 topping the mark 2,200,000 MT per annum.
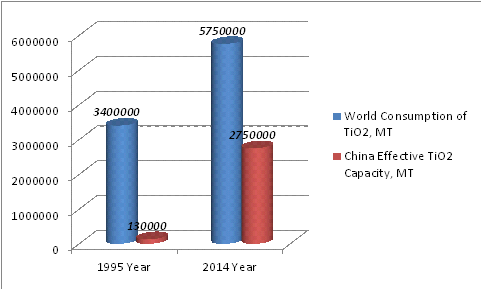
World TiO2 Consumption and China Effective TiO2 Capacity in 1995 and 2014
I personally, in the past 10 years had the opportunity to visit several factories in China built in the early 2000s, in the mid-2000s and the beginning of 2010s, and externally all of them leaves a good impression. The plants that I have seen were fairly modern mainstream process with using modern equipment including the one that a number of leading world companies began to use in the last 10-15 years after the renovations on their enterprises (not a secret that all sulphate factories of leading global companies were constructed over 30 years ago, and the youngest chloride plant of DuPont Company situated in Taiwan in Kuan Yin this year marks the 21). Tellingly on these factories in China which I visited most of the equipment was made inside China by China producers including some production equipment units which are key to the process and quality indicators jf the finished product.
Until 2014 the only company in China, Jinzhou Titanium Industry Co., Ltd. produced titanium dioxide by the chloride technology (plant capacity of 30,000 MT per annum). However, in 2014 by two China Companies were launched plants with a capacity of 60,000 MT per annum for each plant, utilizing the chloride technology for titanium dioxide manufacturing. It is Yunnan Xinli Non-Ferrous Metals Co.,Ltd. and Luohe City Xingmao Titanium Industry Co.,Ltd.

Chloride TiO2 plant of Jinzhou Titanium Industry Co Ltd Photo taken from http://en.jzty.com.cn/imageRepository/d1a30abe-416a-4c75-94ee-744c1e6f9cb8.jpg
In 2015 expected to launch one more chloride plant with capacity of 100,000 MT per annum, belonging to the company Henan Billions Chemicals Co., Ltd.

Chloride TiO2 plant of Yunnan Xinli Non-Ferrous Metals Co Ltd Photo taken from http://www.xinli-ti.com/files/en/edits/20130915/201309151804244248507.jpg
Thus, at the beginning of 2016 Effective Capacity of chloride TiO2 plants in China will amount to 250,000 MT per annum. But what about the quality characteristics of the products of the China titanium dioxide industry? What kind of evolution they have passed for the last 20 years? What is the status of China titanium dioxide industry at the moment, what products it releases, and whether these products satisfy requests of the European and North American markets as well as other markets outside of China? What are the prospects of further development of TiO2 Industry in China? Is the choice of chloride production technology of TiO2 for the China manufacturers without alternative, and what prospect of sulphate plants? These and other questions, we will try to discuss in a series of articles under the title “China titanium dioxide industry: current status and following steps. The technical side of the coin”.

Control room of Chloride TiO2 plant of Luohe City Xingmao Titanium Industry Co Ltd Photo cut out of the video from http://www.xingmaoti.com/en/video_info.aspx?News_Id=63&NewsCateID=56&CateId=56
2. The current state of TiO2 products in China. Comparison with the Top-5 products of western producers of TiO2
2.1. Factors of influence on China industry of TiO2 in the coming years
At the beginning I would like to mention a few important factors that will influence the China titanium dioxide industry in the coming years providing a surplus of supply in the domestic China market which was of course the main driving force of development during the preceding 20 years.
- The decrease of growth dynamics of the China economy. This means that domestic market will become more surplus. Considering that China's producers of TiO2 basically focused on the huge domestic market, to companies would be more and more difficult to get through to the customer, overloaded by proposals of different companies.
- The excess of production capacity. As for 2014 they may be estimated at 450,000 MT or about 24% of the total consumption in 2014 in China of titanium dioxide, while also should be noted that among the consumption of titanium dioxide the 12% was imported into China pigment. This is the second factor of pressure to the side of an increase of surplus on the domestic market.
- Continuation of growth dynamics of production capacity (unless, of course, the growth trend typical for 2014 year – 250,000 MT per annum will maintain). This is the third factor of pressure aimed at increasing the supply of the domestic market.
Judging by the fact that over three years (2011-2013) the volume of exports of the China TiO2 practically unchanged, holding at 400,000-450,000 MT per annum, and in 2014 this figure increased by 30-50% and amounted to 600,000 MT per annum surplus of supply on the domestic market is already pushing China producers to seek foreign markets for their products.
Obviously, this trend will increase. However in foreign markets China products will face difficulties, overcoming of which will be the main task of the next few years for China manufacturers of titanium dioxide, and chief among them is the level of product quality and adaptability of China TiO2 products for various applications. In addition to that, over time, as the further development and complication of the China domestic market and therefore the complexity of inquiries of consumers inside China, with the same difficulties, China manufacturers will face more and more on the domestic market. Probably, these and a number of other not mentioned here factors will significantly alter the appearance of China TiO2 industry in the coming years. And one of such changes will be more and more orienting of the China companies on the consumers outside China.
2.2. Features of the world market of TiO2 in the light of requirements to quality and range of titanium dioxide grades
Certain traditions of a pigment of TiO2 and TiO2 grade range were formed on the outside, in relation to the China markets, primarily in the sophisticated markets such as the European and North American (their total share of world consumption is as at 2014 year about 38%), and secondly, other markets outside China in which transnational companies-consumers of TiO2 were opening their factories and transferred to these markets their requirements for raw materials including TiO2. The formation of these traditions occurred as a result of active cooperation for the past more than three decades between the world's leading manufacturers of titanium dioxide and the world's leading companies which are consumers of TiO2 for different areas of industry such as Paint & Coatings, Plastics and Décor Paper. This has resulted in the formation of a kind of consensus between consumers and producers of TiO2 in quality issues of products, their assortment and defined business practice (deferred payment, convenient logistics, responding to complaints, the willingness to compensate the costs for the supply of products of unsatisfactory quality, etc.).
Nonconformance to these standards, misunderstanding of quality requirements and the reasons exactly of such grade assortment, encompassing all possible applications, and also not following to the certain business practices are a major problem for the expansion of sales of China manufacturers of TiO2. From my personal communication with many big European consumers of titanium dioxide exactly that was the cause of non-cooperation with China companies in question of supply of TiO2. Of course, sometimes a very low price can help to overcome the lack of quality or, for example, poor logistics, but not for all applications or for all occasions. In addition, the factor of low price in recent years is not "cup of tea" of China products, at least in the European and American markets.
So, before analyzing the current state of China industry of TiO2, let's clarify what a consensus emerged on the world markets relative to grade assortment and quality requirements for grades of titanium dioxide, depending on their final application. Questions of business practice, I will not go into detail, about this long time and much written by more experienced authors; our review will focus mainly on the technical side.
In the next few sections are resents a small introduction into the world's leading range of branded non-China producers of Top 5 (DuPont, Huntsman, Cristal, Kronos, Tronox) including the data about typical requirements for the basic quality characteristics of the products depending on their application.
2.2.1. Paint & Coatings application
The world's leading manufacturers of TiO2 have only six basic types of grades of TiO2 for Paint & Coating application. Typical characteristics of these grades, the scope of application and classification in accordance with international standards are presented in Tables 1-6
Table 1. P&C Type 1
|
P&C Type 1 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
94-96% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Electrodeposition paints* Automotive (Primers) Can Coatings Coil Coatings Water-borne and Solvent-borne Industrial and Decorative Coatings Wood Paints Rubber Plastics (usable) Can use in Printing Inks |
*See item 13 |
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
Superior1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Low |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
High |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
10-20 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
<200 µS/cm |
For e-coat applications; for other applications this grade can have conductivity more 200 µS/cm |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
DuPont R-900, Kronos 2020, Tiona 568, Tronox CR-800, Tioxide R-TC-90, Sachtleben RODI, Sachtleben RDI, Sachtleben R-210, Sachtleben R-KB-3 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 2. P&C Type 2
|
P&C Type 2 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
92-94% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina, Silica |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present or not present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Water-borne and Solvent-borne Industrial and Decorative Coatings |
|
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
High1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Medium |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
Medium |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
20-30 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
Approximately 400-600 |
This grade cannot be used for e-coats. |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II, III |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tiona-RK-B-2, DuPont R-902+, Sachtleben R-KB-2 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 3. P&C Type 3
|
P&C Type 3 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
80-86% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina, Silica |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present or not present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Highly pigmented emulsion paints, Exterior and interior trade sales paints, Paper filler and coating applications, Wallpaper coatings, Flat flexographic inks |
|
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
Low1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Superior |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
Low |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97,5 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<1,7 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
20-30 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
Approximately 700-1000 |
This grade cannot be used for e-coats. |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R3 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
III |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tioxide RXL, Kronos 2044, Sachtleben RDDI, DuPont R-931, DuPont TS-6300 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 4. P&C Type 4
|
P&C Type 4 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
94-96% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Printing Inks Can Coatings Coil Coatings Wood Paints Water-born or solvent-born coatings with very high gloss |
|
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
High1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Low |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
Superior |
This grade has also more blue undertone in carbon black undertone test (CBU) in comparison with other P&C grades |
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
5-15 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
Approximately 200-400 |
This grade cannot be used for e-coats. |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tioxide TR-52, Sachtleben RDI-S, Sachtleben R-FD-I, Kronos 2063, Kronos 2090 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 5. P&C Type 5
|
P&C Type 5 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
92-95% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina, Zirconia |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Automotive finishes and refinishes Coil Coatings Powder coatings Marine Coatings Water-born or solvent-born coatings |
|
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
High1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Low |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
High |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
10-20 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
High |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
Approximately 300-500 |
This grade cannot be used for e-coats. |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II, V |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tiona 595, Tioxide TR-92, Kronos 2310, Kronos 2315, Kronos 2190, Tronox CR-828, Sachtleben R-KB-6 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 6. P&C Type 6
|
P&C Type 6 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
91-93% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina, Silica |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Exterior Coatings Automotive Finishes and Refinishes Coil Coatings Powder Coatings Marine Coatings Aerospace Coatings |
|
|
6 |
Opacity in low solid applications |
Medium-High1 |
|
|
7 |
Opacity in high solid applications |
Low |
|
|
8 |
Gloss in high gloss applications |
Medium-High |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility (Based on ISO 8380-3) |
25-35 µ |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
Superior |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Conductivity of extract from slurry of TiO2 according DIN 19529:2009-01) |
Approximately 400-600 |
This grade cannot be used for e-coats. |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II, IV |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
DuPont R-706, DuPont TS-6200, Tiona 596, Tiona-696, Kronos 2160, Kronos 2360, Tronox CR-880, Tronox CR-826 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
2.2.2. Plastic application
The world's leading manufacturers of TiO2 have only three basic types of TiO2 grades for Plastic application. Typical characteristics of these grades, the scope of application and classification in accordance with international standards are presented in Tables 7-9.
Table 7. Plastic Type 1
|
Plastic Type 1 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
97-98% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophobic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Polyolefin Masterbatch Flexible PVC (interior) High Temperature Cast Films Thin Films PVC-plastisols |
|
|
6 |
Relative scattering power |
High1 |
|
|
7 |
Filter Pressure Value Test (FPV test) according EN 13900-5 |
Low-medium |
The lower values are better for use in the masterbatch application |
|
8 |
Carbon Black Undetone |
Blue-very Blue |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>96,5 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility in thermoplastics |
High |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
Low-medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Lacing Resistance |
Superior |
|
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R1 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tioxide R-FK-5, Tioxide TR-23, Tioxide TR-38, Tioxide TR-28, Sachtleben R-FK-2, Tiona-125, Tiona-188, DuPont R-104, Kronos 2230, Kronos 2500, Tronox CR-470, Tronox 834, Tronox 8400 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 8. Plastic Type 2
|
Plastic Type 2 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
95-96% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophobic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
Polyolefin Masterbatch Polyethylene Polypropylene PVC (Interior) PVC (Exterior, Chalking) PVC Pipe ABS Polycarbonate Polystyrene Polyamide |
|
|
6 |
Relative scattering power |
Superior1 |
|
|
7 |
Filter Pressure Value Test (FPV test) according EN 13900-5 |
Low |
The lower values are better for use in the masterbatch application |
|
8 |
Carbon Black Undetone |
very Blue |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility in thermoplastics |
Superior |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
Medium |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Lacing Resistance |
Medium |
|
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
Tiona 90, Sachtleben 405, DuPont R-350, Tiona RL-91, Kronos 2211, Kronos 2233, Kronos 2450, Kronos 2450 |
DuPont R-350 due to the use of special technology has the superior Lacing Resistance (see item 13) |
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Table 9. Plastic Type 3
|
Plastic Type 3 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
91-93% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Alumina, Silica |
Some companies also use Zirconia |
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
Present |
Hydrophobic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
PVC and polyolefines (Exterior, Nonchalking) Agricultural Films Outdoor Furniture PVC-Windows sections |
|
|
6 |
Relative scattering power |
Medium-High1 |
|
|
7 |
Filter Pressure Value Test (FPV test) according EN 13900-5 |
Medium |
The lower values are better for use in the masterbatch application |
|
8 |
Carbon Black Undetone |
Neutral |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility in thermoplastics |
High |
|
|
12 |
Durability (weather ability) |
Superior |
Anatase grades have a low level of durability |
|
13 |
Lacing Resistance |
Low |
|
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R2 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
II, IV |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
DuPont R-105, Tiona 168, Tioxide R-TC30, Kronos 2220, Kronos 2222, Tronox 435, Sachtleben R-FK-3 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
2.2.3. Décor Paper application
The world's leading manufacturers of TiO2 have only one basic type of TiO2 grades for Décor Paper application. Typical characteristics of these grades, the scope of application, and classification in accordance with international standards are presented in Table 10.
Table 10. DP Type 1
|
DP Type 1 |
|||
|
# |
Typical Characteristics |
Decription |
Note |
|
1 |
TiO2 content |
87-90% |
|
|
2 |
Lattice |
>97% of Rutile |
|
|
3 |
Surface Coating |
Aluminium compounds |
|
|
4 |
Organic treatment |
None |
Hydrophilic surface properties |
|
5 |
Applications |
High and Low Pressure Laminate Printing Inks for Décor Paper Melamine moulding powders |
|
|
6 |
Lightfastness (Blue Wool Scale) according to DIN EN 13329, DIN 54004 |
>6 |
Usually 6-7…7; Rutile grades for other application even with superior durability (weatherability) have Lightfastness <6 (usually 3-5) and can be used for this application only in limited quantities |
|
7 |
Opacity |
High1 |
|
|
8 |
pH of isoelectric point. |
>6,0 |
|
|
9 |
L* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
>97 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
10 |
b* (CIELAB) in pressed powder |
<2 |
D65, Spectrophotometer are normalized by Net Profiler 3 tool - http://www.xrite.com/netprofiler-3-software |
|
11 |
Dispersibility in water |
High |
For purposes of paper making |
|
12 |
Retention on the paper fiber |
High |
|
|
13 |
Heat Resistance |
High |
180 degree С/15 minute |
|
14 |
ISO 591-1:2000 type |
R3 |
|
|
15 |
ASTM D 476-00 (2005) types |
IV |
|
|
16 |
Analogous grades of Top-5 Western Companies |
DuPont R-796+, Sachtleben R-PL-2, Sachtleben R-610L, Tronox 820, Kronos 2800, Tiona RCL-722 |
|
|
References: 1 Here and hereafter for other parameters we are using relative estimations: low-medium-high-superior |
|||
Thus, in Tables 1-10 is characterized a whole range of rutile titanium dioxide grades manufactured by the world's leading manufacturers and by 100% satisfying all customer needs of rutile TiO2 pigment in world markets of TiO2 including Europe and North America.
Now let's turn to China and analyze what an arsenal of products for which applications and what quality have Top China companies, and also other members of the China TiO2 industry and compare it with that what offered by leading global companies. This will allow us to clarify how much prepared the China TiO2 industry to compete with the world's leading companies and in what aspects it is necessary to make changes to improve their competitiveness, and for a number of China TiO2 companies these changes will generally be a matter of survival.